Global Warming Causes Nights To Become Hotter Than Days
Harin - Oct 09, 2020
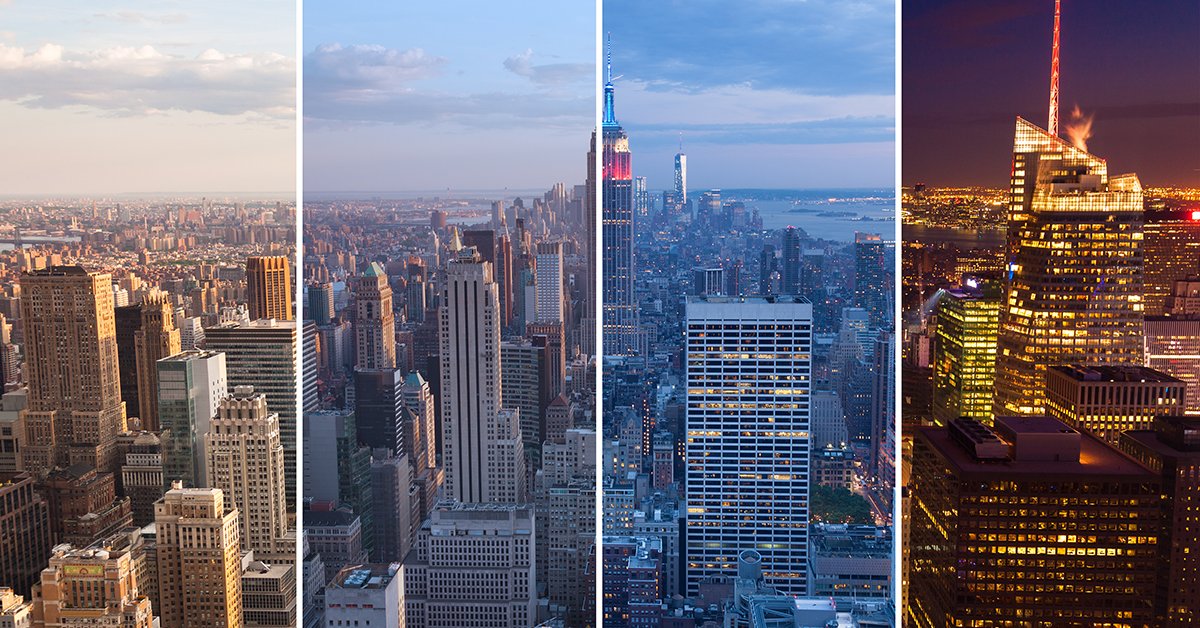

The study from scientists of the University of Exeter emphasizes how daytime and night-time temperatures are being affected differently by global warming.
- The Earth Is At Its Hottest It Has Ever Been In At Least 12,000 Years
- 10,000 Square Meters Of White Covering Is Preventing The Ice From Melting
- We Just Experienced The Hottest January Ever Since 11,700 Years Ago
A new study warns of global warming causing a “warming asymmetry” between days and nights. It suggests that compared to day-time temperatures, there is an increase in night-time temperatures.
Scientists from the University of Exeter researched data from 1983 to 2017 to come to this conclusion. They examined hourly records of temperature, humidity, cloud cover, and precipitation.

The study can be found in the Global Change Biology journal. In the study, they mentioned how they discovered a 0.25 Celcius-degree difference in annual temperature between days and nights. They observed the pattern in more than 50% of the global land surface.
The study emphasizes how daytime and night-time temperatures are being affected differently by global warming. In some areas, the temperatures during the nights rose more quickly. Meanwhile, night-time temperatures soar higher in other locations.
However, the total area of greater night-time warming was two times larger.
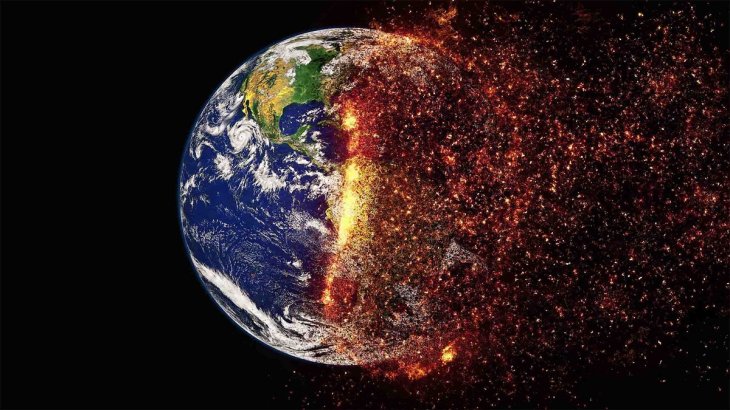

The study points to the changing levels of cloud cover as the reason for warming asymmetry between the temperatures of days and nights.
During the day, when a cloud cover increases, the surface is cool. However, at night, the same cloud cover will entrap heat, raising the temperature.
A decreased cloud cover during the day will allow more heat. But at night, the warmth is lost.
Warming asymmetry can potentially affect the natural world, especially species that are only active during the day or at night.
>>> We Just Experienced The Hottest January Ever Since 11,700 Years Ago
Featured Stories

Features - Jan 29, 2026
Permanently Deleting Your Instagram Account: A Complete Step-by-Step Tutorial

Features - Jul 01, 2025
What Are The Fastest Passenger Vehicles Ever Created?

Features - Jun 25, 2025
Japan Hydrogen Breakthrough: Scientists Crack the Clean Energy Code with...

ICT News - Jun 25, 2025
AI Intimidation Tactics: CEOs Turn Flawed Technology Into Employee Fear Machine

Review - Jun 25, 2025
Windows 11 Problems: Is Microsoft's "Best" OS Actually Getting Worse?

Features - Jun 22, 2025
Telegram Founder Pavel Durov Plans to Split $14 Billion Fortune Among 106 Children

ICT News - Jun 22, 2025
Neuralink Telepathy Chip Enables Quadriplegic Rob Greiner to Control Games with...

Features - Jun 21, 2025
This Over $100 Bottle Has Nothing But Fresh Air Inside

Features - Jun 18, 2025
Best Mobile VPN Apps for Gaming 2025: Complete Guide

Features - Jun 18, 2025
A Math Formula Tells Us How Long Everything Will Live
Read more

Gadgets- Mar 08, 2026
Best Budget Keyboards of 2026
These budget keyboards prove that you don't need to spend hundreds for a quality typing experience in 2026.
Comments
Sort by Newest | Popular