Top 21 Most Significant Data Breaches Of 2018
Harin - Jan 01, 2019

2018 is the year where it seems like data breaches in which customers’ personal information may have been compromised happened every week.
- Google's Project Toscana: Elevating Pixel Face Unlock to Rival Apple's Face ID
- Google Offers Voluntary Buyouts to US Employees Amid AI Push
- Google SynthID: Everything You Need to Know About AI Content Detection
2018 is the year where it seems like data breaches in which customers’ personal information may have been compromised happened every week.

There are numerous reasons why data breaches happen. It may be hackers, data mishandling or selling to third parties. Holes in the security system of a website can lead to information unprotected.
Marriott hotel was one of the latest cases, which revealed that approximately 500 million customers’ information had been accessed.
Some of 2018’s biggest victims that should be mentioned are Orbitz, Google, Quora, and T-Mobile. Facebook’s major breaches lead to the compromise of 100 million users’ data.
This is the list of the most significant data breaches of 2018:
21. British Airways – 380,000

What: Card payments
When: From August 21, 2018, to September 5, 2018
How: bookings made on the airline’s app and website were affected by a “criminal” hack.
20. Orbitz – 880,000
What: Personal data as well as payment cards info like emails, phone numbers, and billing addresses.
When: From January 1, 2016, to December 22, 2017
How: Hackers gained access to travel bookings in the system of the website.
19. SingHealth – 1.5 million

What: Names and addresses in the health database of the Singapore government as well as the dispensed medicines history of some patients. The specific target was the information about Singapore’s prime minister.
When: From May 1, 2015, to July 4, 2018
How: As stated in a statement, a well-planned, targeted, deliberate attack was orchestrated by the hackers.
18. T-Mobile – about 2 million

What: Personal data and encrypted passwords like emails, billing information, and account numbers.
When: August 20, 2018
How: Through an API, an international group of hackers gained access to the servers of T-Mobile.
17. myPersonality – 4 million
What: Personal data of Facebook customers using the myPersonality app.
When: Before 2012, the app was still active, but in April this year, it has been removed from Facebook.
How: The app misused data of Facebook users by allowing researchers and companies to access information with only limited protections.
16. Saks and Lord & Taylor – 5 million

What: payment card numbers
When: The information was never disclosed.
How: Gimini Advisory LLC, a security company based in New York says that JokerStash, a hacking group made an announcement that last week, it had posted for sale over 5 million stolen debit and credit cards. The hacking group also mentioned that the compromised data was from the customers of Saks and Lord & Taylor.
15. SheIn.com – 6.42 million
What: Email addresses as well as encrypted passwords for online store accounts of customers.
When: June 2018
How: Hackers attacked its computer network.
14. Cathay Pacific Airways – 9.4 million
What: 27 credit card numbers with no CVV, 403 expired credit card numbers, 245,000 Hong Kong identity card numbers, and 860,000 passport numbers.
When: The activity was found out in March 2018.
How: hackers accessed the data of passengers without authorization
13. Careem – 14 million

What: trip data as well as names, phone numbers and email addresses.
When: January 14, 2018
How: The hackers gained access to a computer system storing driver account and customer information.
12. Timehop – 21 million

What: names, phone numbers and email addresses.
When: From December 2017 to July 2018
How: The hackers gained access to the website’s cloud computing environment after getting an access credential. The site didn’t use multifactor authentication to protect its cloud computing account.
11. Ticketfly – 27 million
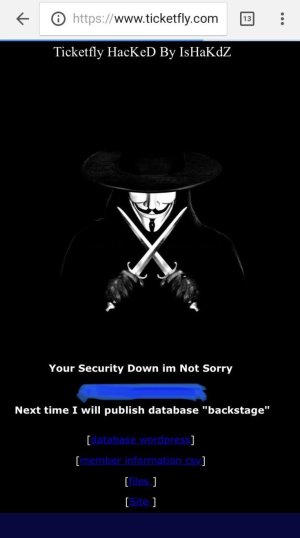
What: Personal information which includes names as well as addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
When: Late May 2018
How: Hacker “IsHaKdZ” attacked that webmaster of the site. He was then capable of accessing a database called “backstage” containing client information like festivals, venues, and promoters that use services of Ticketfly.
10. Facebook – 29 million

What: Highly sensitive information from contact details, relationship status, locations, recent searches, and devices used.
When: From July 2017 to September 2018
How: The hackers were capable of taking advantage of Facebook’s code to take the “access tokens”. These tokens are the digital keys allowing them to hack into users’ accounts.
9. Chegg – 40 million

What: Personal information which includes names, account usernames along with the passwords, email addresses, and shipping addresses.
When: From April 29, 2018, to September 19, 2018
How: As stated in SEC filing of Chegg, an unauthorized party accessed a database of the company hosting user info for chegg.com as well as other family brands of the company like EasyBib.
8. Google – 52.5 million

What: Google+ profiles’ private data, from names, job titles, employers, email addresses to ages, birth dates and relationship statuses.
When: From 2015 to March 2018 and from November 7, 2018, to November 13, 2018
How: Earlier, after the Wall Street Journal reported that a software error led to the exposure of 500,000 Google+ users’ personal information, Google has made an announcement that Google+ would be shut down. Again in December, Google announced that it had been attacked again with 52.5 million users affected. In April 2019, Google+ will be shut down indefinitely.
7. Cambridge Analytica – 87 million
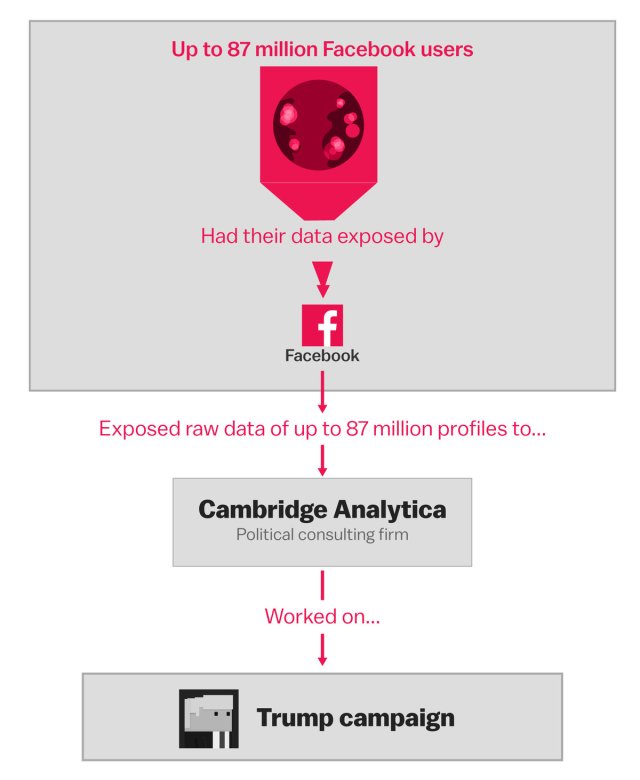
What: Facebook data and profiles which identify users’ interests and preferences.
When: 2015
How: A professor at the University of Cambridge developed an app known as “thisisyourdigital life,” which improperly shared users’ data to third parties including Cambridge Analytica. This is the firm specialized in data analyzing which assisted the presidential campaign of President Trump by making use of millions of voter’s data to create targeted ads.
The app was installed by only 270,000 users. However, because of data sharing regulations of Facebook at that time, the app could also gather information from their friends.
6. MyHeritage – 92 million

What: Users’ email addresses as well as encrypted passwords.
When: October 26, 2017
How: The hackers gained access to users email addresses and their passwords after successfully attacking a private server located outside of the firm.
5. Quora – 100 million
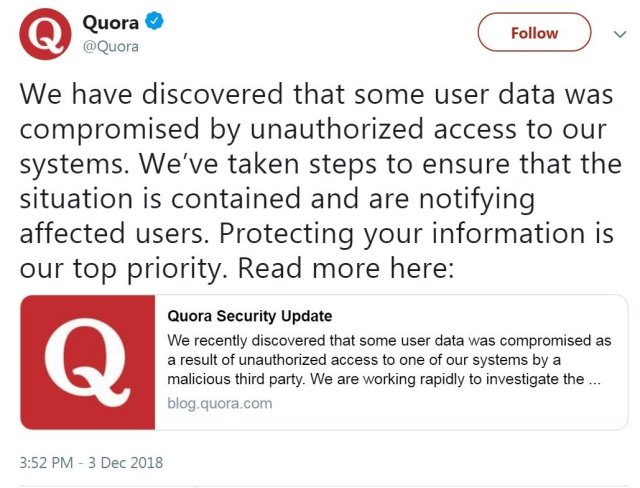
What: Account data, from names to email addresses, along with encrypted passwords. Info of user accounts which linked to the website as well as their public questions and responses were also attacked.
When: The breach was found out in November 2018.
How: One of the website’s systems was accessed by a malicious third party.
4. MyFitnessPal – 150 million
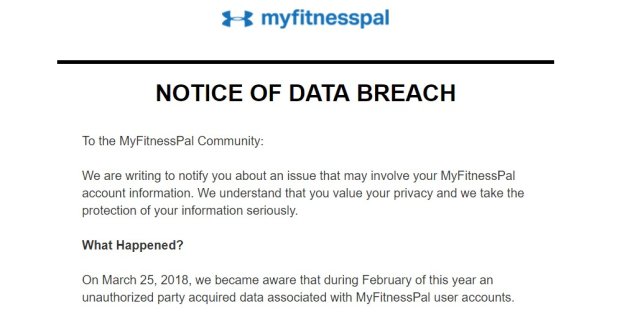
What: Usernames as well as email addresses and passwords.
When: February 2018.
How: An unapproved party was able to access user accounts’ data on MyFitnessPal, a fitness app owned by Under Armour.
3. Exactis – 340 million
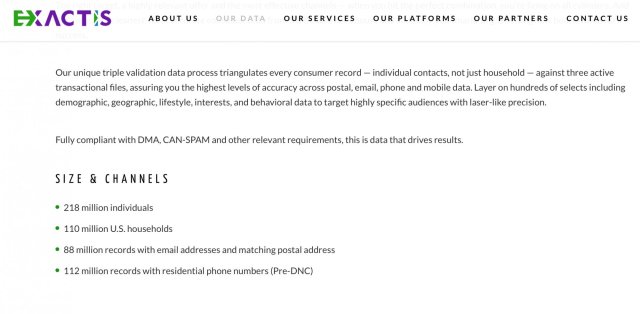
What: Data of millions of businesses and people including addresses, phone numbers, personal characteristics and interests and many more.
When: June 2018
How: A database with details of almost every US citizen was spotted being left exposed on an accessible server by a security expert. However, it is still not clear if any hackers gained access to the data.
2. Marriott Starwood hotels – 500 million

What: Information of the guests which include reservation dates, payment card numbers along with their expiration dates, phone numbers, passport numbers, and email addresses.
When: From 2014 to September 2018
How: The hackers were able to access the database for reservation of Marriot’s Starwood hotels. This info was then copied and stolen.
1. Aadhar – 1.1 billion
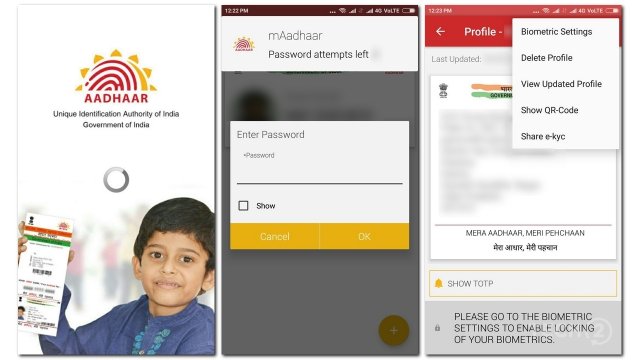
What: Private data of India citizens, from their names, 12-digit ID numbers to their connected services such as bank accounts.
When: The incident was found out in March 2018.
How: A data leak of Indane, a state-owned utility company, led to identity as well as biometric info of India citizens got exposed. Indane hadn’t made sure to secure their API used for database access, which allowed anyone to access Aadhar data.
Featured Stories

Features - Jan 29, 2026
Permanently Deleting Your Instagram Account: A Complete Step-by-Step Tutorial

Features - Jul 01, 2025
What Are The Fastest Passenger Vehicles Ever Created?

Features - Jun 25, 2025
Japan Hydrogen Breakthrough: Scientists Crack the Clean Energy Code with...

ICT News - Jun 25, 2025
AI Intimidation Tactics: CEOs Turn Flawed Technology Into Employee Fear Machine

Review - Jun 25, 2025
Windows 11 Problems: Is Microsoft's "Best" OS Actually Getting Worse?

Features - Jun 22, 2025
Telegram Founder Pavel Durov Plans to Split $14 Billion Fortune Among 106 Children

ICT News - Jun 22, 2025
Neuralink Telepathy Chip Enables Quadriplegic Rob Greiner to Control Games with...

Features - Jun 21, 2025
This Over $100 Bottle Has Nothing But Fresh Air Inside

Features - Jun 18, 2025
Best Mobile VPN Apps for Gaming 2025: Complete Guide

Features - Jun 18, 2025
A Math Formula Tells Us How Long Everything Will Live
Read more

ICT News- Mar 05, 2026
X Platform Implements Strict Measures Against Fake AI-Generated Videos Amid Iran Conflict
In the meantime, users are advised to scrutinize sources, check for AI indicators, and rely on verified news outlets.

Mobile- Mar 06, 2026
Samsung Galaxy S26 Series Sets New Pre-Order Records: Ultra Model Captures 70 Percent of Sales
With such robust initial demand, the Galaxy S26 series is poised to outperform its predecessors in total sales, solidifying Samsung's dominance in the premium smartphone market.

Mobile- Mar 07, 2026
Xiaomi Unveils Cutting-Edge 17 Series Smartphones and Teases Vision GT Hypercar
Xiaomi's MWC 2026 presentation highlights its ambition to dominate not just smartphones but also connected ecosystems and electric vehicles.

How To- Mar 04, 2026
Getting Started with AI: A Newbie's Simple Guide
Are you curious about artificial intelligence but not sure where to begin? You are not alone.
Comments
Sort by Newest | Popular