NASA Spacecraft Travelling Through Space Calls For Help From Earth
Anil - Jan 31, 2020

The NASA spacecraft, Voyager 2, is suffering a technical hiccup. Engineers are trying to send all the instructions as well as repair processes from billions of miles away.
- Russia Will Build A Lunar Space Station With China Because It's Done With NASA
- NASA Reveals 20 Most Stunning Earth Images Taken From The ISS
- Indian-Origin NASA Researcher Discovers Jupiter Moon Europa Glows In The Dark
No system is perfect, so not only do we focus on building or upgrading it but we also have to contemplate all the potential cases that could unfortunately occur, especially we refer to a spacecraft going into orbit. NASA, the American space agency, has started collaborating with engineers to repair technical difficulties on its Voyager 2 spacecraft. Notably, the NASA spacecraft is currently flying across interstellar space and all the instructions for repairment will be conducted from billions of miles away.

Specifically, Voyager 2 unintentionally triggered the autonomous fault protection routines while it was attempting to complete a regularly scheduled maneuver. In fact, the spacecraft will activate this mechanism once a technical issue happens in order to limit further damage. This time, an error somehow enabled two power-hungry systems to operate simultaneously, leading to the power overload in the spacecraft’s energy supply system - according to engineers who are currently responsible for NASA’s Voyager project.
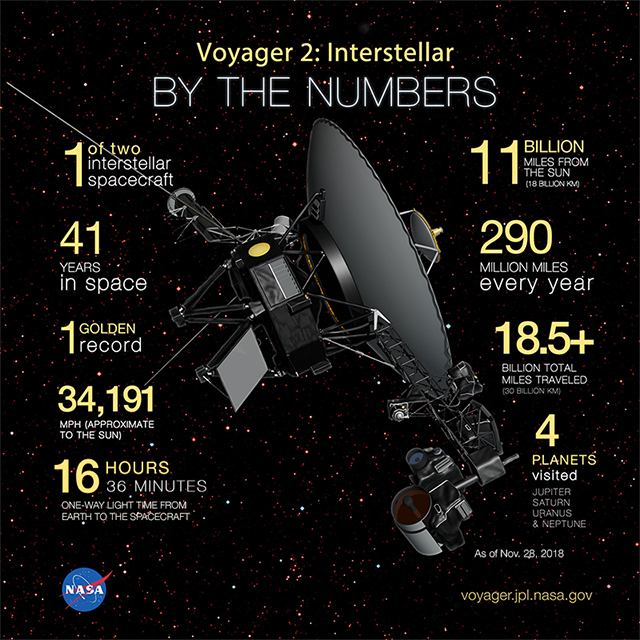
In general, this NASA spacecraft is about 11.5 billion miles far away from Earth, the fix turns out to be a tricky business in terms of either distance or time. These engineers have since tried to turn off one of the two power-hungry systems, but it seems to be more difficult as they have got no data from Voyager 2 since January 28. Apparently, the final target of restoring normal operations requires them to work a lot more.

Given that commanding signals between the spacecraft and the team nearly reach the speed of light, it won’t cross the lengthy distance within 17 hours. Doubling this figure, it takes around 34 hours of waiting to evaluate the responding result after engineers send their instructions to the spacecraft.
Featured Stories

Features - Jan 29, 2026
Permanently Deleting Your Instagram Account: A Complete Step-by-Step Tutorial

Features - Jul 01, 2025
What Are The Fastest Passenger Vehicles Ever Created?

Features - Jun 25, 2025
Japan Hydrogen Breakthrough: Scientists Crack the Clean Energy Code with...

ICT News - Jun 25, 2025
AI Intimidation Tactics: CEOs Turn Flawed Technology Into Employee Fear Machine

Review - Jun 25, 2025
Windows 11 Problems: Is Microsoft's "Best" OS Actually Getting Worse?

Features - Jun 22, 2025
Telegram Founder Pavel Durov Plans to Split $14 Billion Fortune Among 106 Children

ICT News - Jun 22, 2025
Neuralink Telepathy Chip Enables Quadriplegic Rob Greiner to Control Games with...

Features - Jun 21, 2025
This Over $100 Bottle Has Nothing But Fresh Air Inside

Features - Jun 18, 2025
Best Mobile VPN Apps for Gaming 2025: Complete Guide

Features - Jun 18, 2025
A Math Formula Tells Us How Long Everything Will Live
Read more

ICT News- Mar 03, 2026
Budget Entry-Level PCs Under $500 to Vanish by 2028 Due to Memory Price Surge
The era of the sub-$500 PC appears to be ending.

ICT News- Mar 02, 2026
IDC Report Predicts Surging Smartphone Prices Due to Global RAM Shortage
This development underscores the broader ripple effects of the AI boom on everyday technology, highlighting the interconnected nature of global semiconductor supply chains.

ICT News- Mar 01, 2026
Samsung Links Galaxy S26 Price Hikes to AI Memory Supply Issues
This development highlights the broader challenges faced by the tech industry as it integrates artificial intelligence into everyday consumer electronics.
Comments
Sort by Newest | Popular