This Chip From Intel Will Make Quantum Computers Commercially Available
Aadhya Khatri - Dec 13, 2019
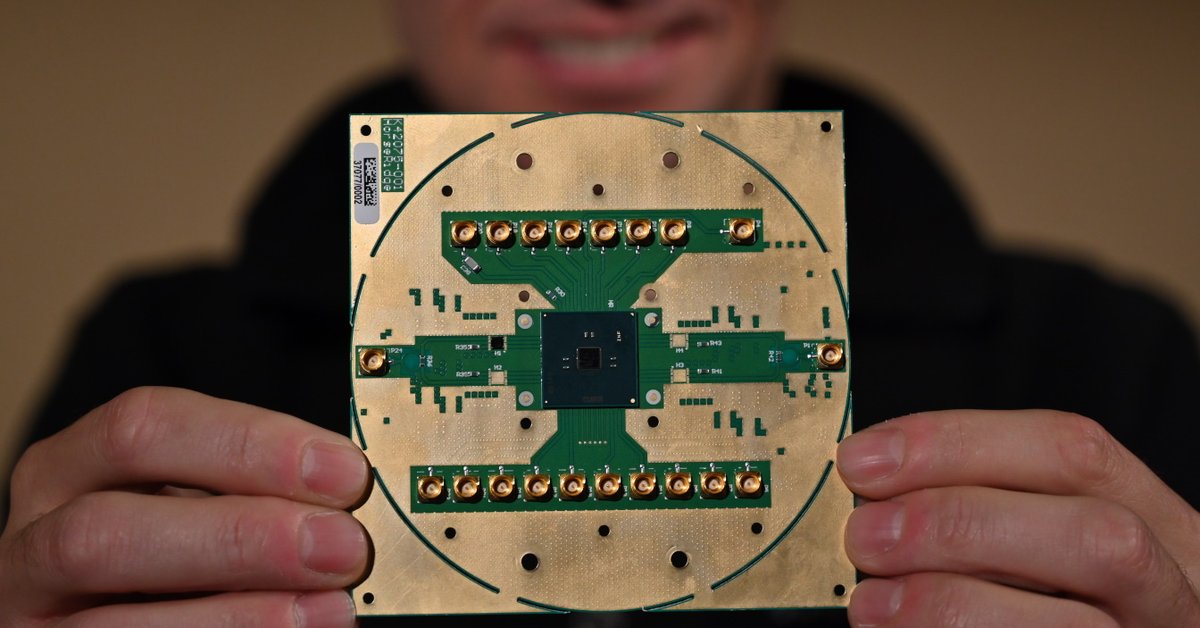
The new chip is called Horse Ridge by Intel, named after the region with the lowest temperature in Oregon. It manages quantum computers’ cooling
- Stunning Math Motifs Found On The Pillars Of The Marundheeswarar Temple In Chennai
- India Commits To Quantum Computing Research With An Investment Of ₹8000 Crores
- LEGO Blocks Are Found To Be An Excellent Material To Build Quantum Computers
Despite all the achievements made recently, quantum computers are still at the infant stage of development. Microsoft, Google, IBM, and other companies interested in this field have Intel to thank for its latest chip, which can make managing qubits much simpler.
The new chip is called Horse Ridge, named after the region with the lowest temperature in Oregon. The name is also a reference to what it does, which is to manage quantum computers’ cooling.
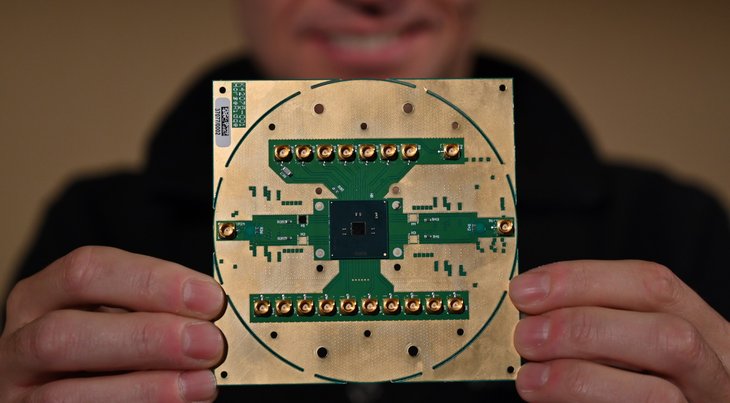
As stated by Intel, the new chip is made to simplify the management and control of the quantum circuit. It is as big as a coffee cup coaster but it can take over the job of an external device.
The production of the chip has the participation of QuTech’s research partners and the 22nm FinFET technology of Intel. The chip is the answer to the biggest obstacle to make quantum computing commercially available, interconnections and electronic controls.
Horse Ridge is able to lower the complexity of the engineering of quantum control, reducing the quantity from a refrigerator with hundreds of cables leaving and entering to one unit only working close to the quantum device.
The qubit control in the cryogenic cooler is simplified as the chip can also be a processor for radio frequencies. Intel programs Horse Ridge with the instructions corresponding to the operations of the qubit.
As a cooler that can keep the whole device working at around -273.15 degrees Celsius is a vital part in a quantum computer. Intel’s chip is designed to have certain features allowing them to operate at that specific temperature.
This is why Intel wants to make the chip work on and silicon spin qubits and cryogenic controls at that same temperature, reducing the need for cooling.
Featured Stories

Features - Jan 29, 2026
Permanently Deleting Your Instagram Account: A Complete Step-by-Step Tutorial

Features - Jul 01, 2025
What Are The Fastest Passenger Vehicles Ever Created?

Features - Jun 25, 2025
Japan Hydrogen Breakthrough: Scientists Crack the Clean Energy Code with...

ICT News - Jun 25, 2025
AI Intimidation Tactics: CEOs Turn Flawed Technology Into Employee Fear Machine

Review - Jun 25, 2025
Windows 11 Problems: Is Microsoft's "Best" OS Actually Getting Worse?

Features - Jun 22, 2025
Telegram Founder Pavel Durov Plans to Split $14 Billion Fortune Among 106 Children

ICT News - Jun 22, 2025
Neuralink Telepathy Chip Enables Quadriplegic Rob Greiner to Control Games with...

Features - Jun 21, 2025
This Over $100 Bottle Has Nothing But Fresh Air Inside

Features - Jun 18, 2025
Best Mobile VPN Apps for Gaming 2025: Complete Guide

Features - Jun 18, 2025
A Math Formula Tells Us How Long Everything Will Live
Read more

Mobile- Mar 06, 2026
Samsung Galaxy S26 Series Sets New Pre-Order Records: Ultra Model Captures 70 Percent of Sales
With such robust initial demand, the Galaxy S26 series is poised to outperform its predecessors in total sales, solidifying Samsung's dominance in the premium smartphone market.

Mobile- Mar 07, 2026
Xiaomi Unveils Cutting-Edge 17 Series Smartphones and Teases Vision GT Hypercar
Xiaomi's MWC 2026 presentation highlights its ambition to dominate not just smartphones but also connected ecosystems and electric vehicles.

ICT News- Mar 05, 2026
X Platform Implements Strict Measures Against Fake AI-Generated Videos Amid Iran Conflict
In the meantime, users are advised to scrutinize sources, check for AI indicators, and rely on verified news outlets.
Comments
Sort by Newest | Popular