Scientists Have Found A Way To Produce Breathable Oxygen On Mars
Maya Bhagat - Jun 17, 2019

The very first condition for astronauts to survive Mars with its harsh environment is the air. And, of course, oxygen is the indispensable element.
- Believe It Or Not, Dirt From Mars Can Be Bought With Only $20 A Kilogram
- Elon Musk Doesn't Buy Luxury Vacation Homes, Here's How He Spends His Money
- The First Helicopter To Fly On Mars Is As Small As A Tennis Ball
Technology is more and more developed and the inevitable trend is towards space. Human has the ambition of conquering the universe; therefore, learning about some planets like Mars, Venus and so on is understandable. Nowadays, not only NASA but also other private space companies are attempting to take people to Mars.
The very first condition to carry out this project is astronauts’ ability to survive on Mars with its harsh environment. And, of course, oxygen is the indispensable element.
It is good news that a scientists group is likely to have found a method of generating oxygen. This will contribute a lot to Mars missions in the future as it will allow travelers not to prepare the supplies themselves to survive on Mars.

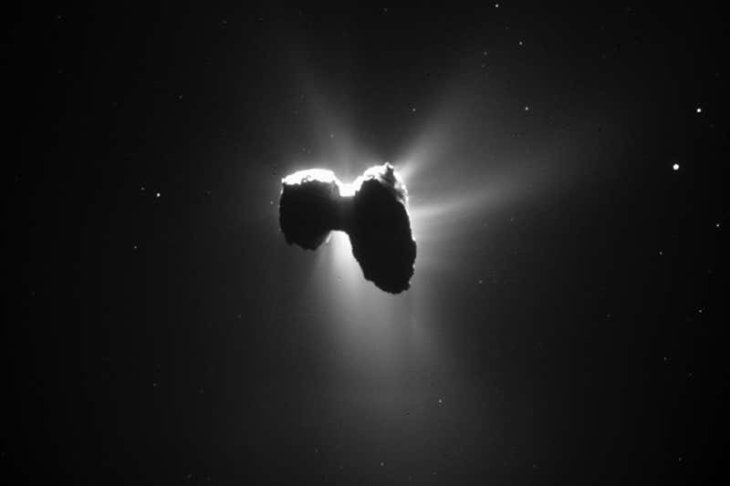
By doing research about comets, a research team’s members from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena were inspired to discover a new technique.
Comets are actually icy rocks which hurtle through space. Their origin is from the Oort Cloud – our solar system’s area that is quite far from the orbit of Neptune. Do you wonder why they have their sparkle tails? It is because some of their ice is burnt as their orbits are asymptotic to the Sun. It is said that they are able to sweep for the huge length of thousands of kilometers.
Now, the way comets generate oxygen must involve kinetic energy. At the moment of the comet’s crash in space, the sublimation process happens in which the ice is burnt due to the sun’s heat. This results in water molecules. And under the impact of static inertia, they will be speedily shoved into the surface of the comet. If the comet’s surface has the compounds which are rich in oxygen, oxygen atoms will be split by the water molecules to create molecular oxygen.

Currently, there is another method to generate oxygen theorized. It is said to relate to the reactions of carbon dioxide. Conducted by Konstantinos Giapis - Caltech chemical engineering professor together with Yunxi Yao - former Caltech postdoctoral fellow, this method is simulated by observing carbon dioxide’ reactions in gold foil. Because the oxidization does not happen in gold foil, molecular oxygen should not be released itself. However, in the case of CO2 speedily hitting the foil, molecular oxygen is produced on the surface of gold
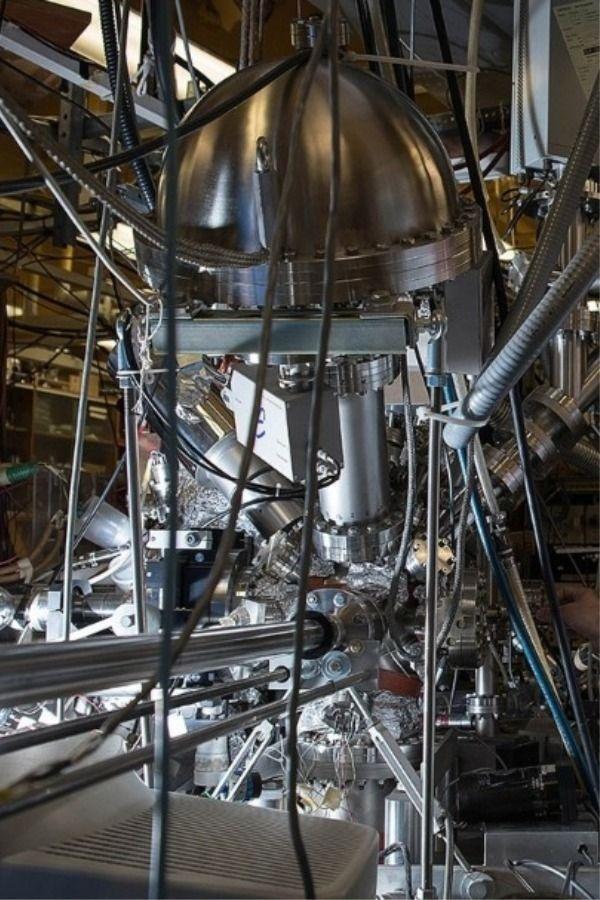

The representatives of Caltech said:
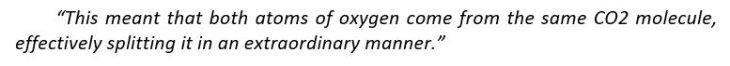
He also clarified the process by showing a simple example. It is throwing a stone at CO2 at the speed of an asteroid or comet traveling through space.
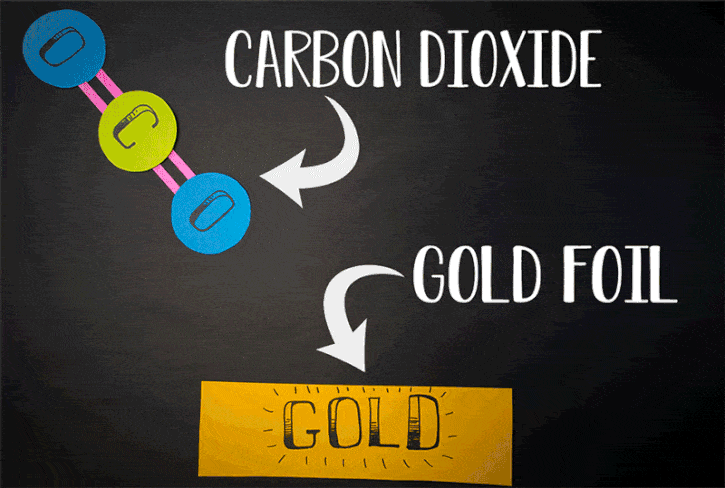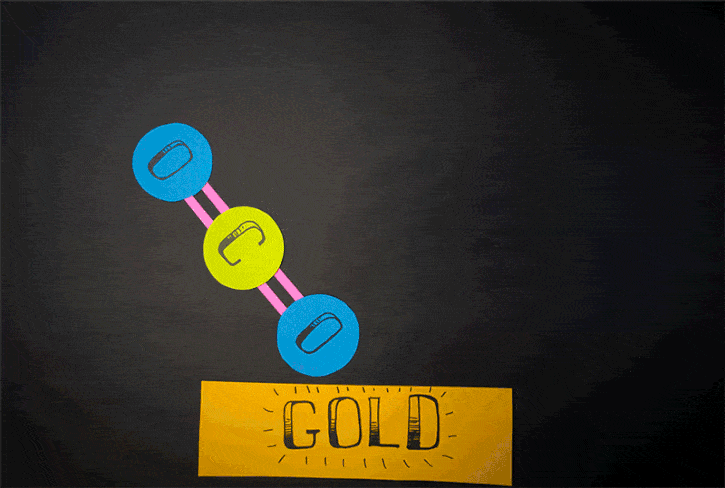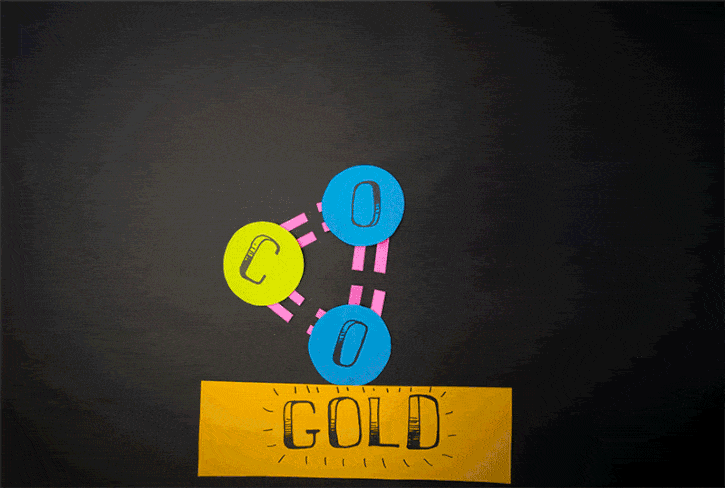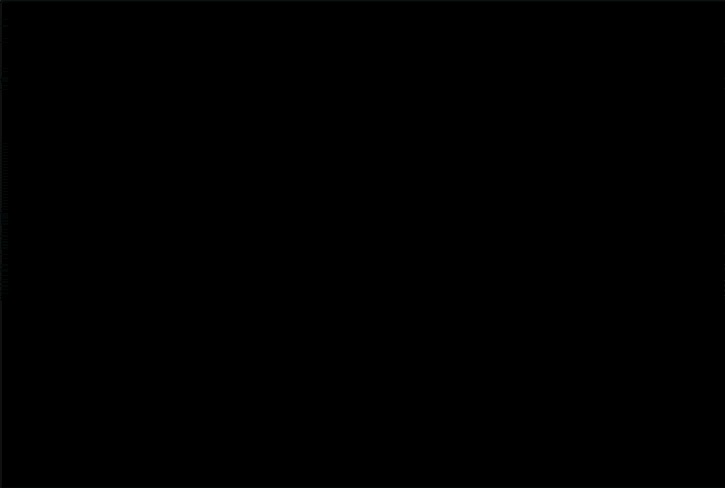
Scientists previously assumed that oxygen found the atmosphere on Mars is assumed to be from the reactions of carbon dioxide hit by the sun’s ultraviolet light. Nonetheless, according to the new theory, its origin may be from the process of dust particles hurtling carbon dioxide molecules at high speed.
Now, experimentally, 100 carbon dioxide molecules can generate only 1 or 2 oxygen molecules. It is such a low yield of oxygen. But it is believed that astronauts can have enough breathable air to survive on Mars in the future thanks to the reactor’s improvement.
This can also be useful for our Earth as it can be used to replace CO2 with oxygen in the atmosphere. It is considered a great way to protect our environment.
Featured Stories

Features - Jan 29, 2026
Permanently Deleting Your Instagram Account: A Complete Step-by-Step Tutorial

Features - Jul 01, 2025
What Are The Fastest Passenger Vehicles Ever Created?

Features - Jun 25, 2025
Japan Hydrogen Breakthrough: Scientists Crack the Clean Energy Code with...

ICT News - Jun 25, 2025
AI Intimidation Tactics: CEOs Turn Flawed Technology Into Employee Fear Machine

Review - Jun 25, 2025
Windows 11 Problems: Is Microsoft's "Best" OS Actually Getting Worse?

Features - Jun 22, 2025
Telegram Founder Pavel Durov Plans to Split $14 Billion Fortune Among 106 Children

ICT News - Jun 22, 2025
Neuralink Telepathy Chip Enables Quadriplegic Rob Greiner to Control Games with...

Features - Jun 21, 2025
This Over $100 Bottle Has Nothing But Fresh Air Inside

Features - Jun 18, 2025
Best Mobile VPN Apps for Gaming 2025: Complete Guide

Features - Jun 18, 2025
A Math Formula Tells Us How Long Everything Will Live
Read more

ICT News- Mar 14, 2026
Elon Musk's High-Stakes $109 Billion Lawsuit Against OpenAI and Microsoft
This could reshape AI partnerships and nonprofit-to-for-profit shifts, echoing Musk's AI safety concerns.
Comments
Sort by Newest | Popular